If you’ve ever wondered about the difference between a “business plan” and a “business model,” you’re not alone. These terms get thrown around a lot in the business world, and it’s time we unravel the mystery.
A business model is a strategic overview of how a business intends to be profitable. In contrast, a business plan is a detailed document that provides step-by-step instructions for implementing that strategy.
In other words, think of your business model as the grand blueprint for your success and the business plan as your boots-on-the-ground guide to making it happen.
Both are important for a successful business. Both work together, with the business model setting the foundation and the business plan guiding the execution.
Today, we will break it down without fancy jargon or complicated concepts. By the end of this read, you’ll have a crystal-clear understanding of what sets these two apart and why it matters to you, whether you’re a seasoned pro or just starting your entrepreneurial journey.
So, grab a seat, and let’s demystify “Business Plan vs. Business Model” in plain and simple terms. Ready?
Business model, business plan, what is the difference?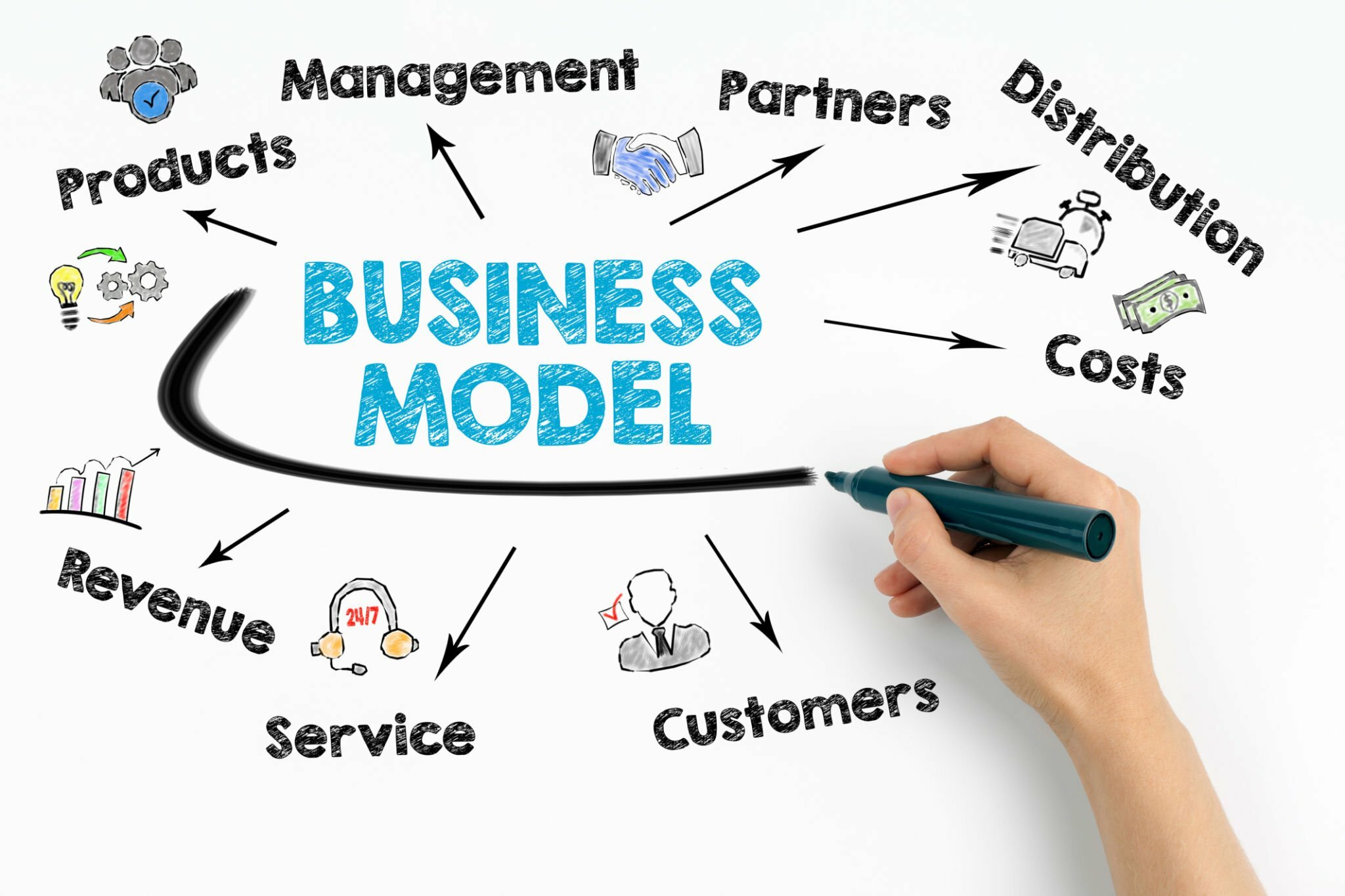

Business Model
At its core, a business model is the conceptual framework that defines how a company creates, delivers, and captures value. It is the big-picture strategy that sets the direction for your business.
Essentially, your business model is your business’s “what” and “why,” providing a strategic direction. It’s a high-level view of how you intend to generate revenue.
Here’s what you need to know about business models:
Customer Segments: Identifying your ideal customer is important. Your business model should help you with distinguishing your audience.
Revenue Streams: How will you generate money through that business? Your model should be the key factor that helps you scale your business by outlining the areas and sources where you can generate revenue, whether through sales, subscriptions, advertising, or other means.
Key Resources and Activities: What critical assets and actions are required to deliver your value proposition? Your business model should pinpoint these key components.
Channels and Customer Relationships: How will you reach and interact with your customers? This section of your model addresses the distribution and customer engagement strategies.
Cost Structure: Running a business incurs costs. Your business model should detail the resources and activities associated with these costs.
Business Plan
On the other hand, a business plan is a detailed blueprint for executing that model. This comprehensive document takes a deeper dive into various aspects of your business. The “how” and “when” and offer a step-by-step guide to executing your business model.
Here’s what a business plan encompasses:
Description of the Business: An overview of your business, its history, mission, and vision, its purpose, and benefits for your customers.
Market Analysis: A detailed examination of your industry, market trends, and competitors.
Funding Needs: If you’re seeking investment, your business plan should specify the amount you need and how you’ll use it.
Marketing and Sales Strategies: How you plan to attract and retain customers and your sales approach.
Operational Plan: The nitty-gritty of how your business will operate, including production processes, supply chain management, and more.
Financial Projections: Forecasts for revenue, expenses, and profits. This is often a key section for attracting investors.
The difference between a business model and a business plan.
Business Model
Purpose
A business model outlines the fundamental strategy for how a business creates, delivers, and captures value. It focuses on the core concept of how the business will operate and be profitable.
Level of Detail
It provides a high-level view of the business, covering customer segments, value propositions, revenue streams, and key resources. It’s a conceptual framework.
Business Plan
Purpose
A business plan is a comprehensive document that serves as a roadmap for executing the business model. It includes detailed strategies, tactics, financial projections, and operational plans.
Level of Detail
It delves deeply into specific areas, such as market analysis, marketing strategies, operational processes, and financial forecasts. It is a detailed, actionable document.
A business model is a strategic overview of how a business intends to be profitable. In contrast, a business plan is a detailed document that provides step-by-step instructions for implementing that strategy. Both are important for a successful business, with the business model setting the foundation and the business plan guiding the execution.
Example of Business Model
These are just a few examples of different business models. Each model has its advantages and challenges, and the choice of model often depends on the specific industry, market, and business goals.
Direct-to-Consumer (DTC) Business Model
Example: Warby Parker
Description: Warby Parker, an eyewear company, follows a DTC business model. They design, produce, and sell eyeglasses directly to consumers through their website and physical retail stores. This model eliminates the need for intermediaries and provides cost savings to customers.
Brick-and-Mortar Business Model
Example: Starbucks
Description: Starbucks operates a brick-and-mortar business model with a vast network of coffee shops worldwide. Customers visit physical stores to buy coffee, beverages, and food. This model focuses on in-person customer experiences.
Subscription-Based Business Model
Example: Netflix
Description: Netflix uses a subscription-based model, where customers pay a monthly fee for unlimited access to streaming content. This model creates recurring revenue and customer loyalty.
Freemium Business Model
Example: Dropbox
Description: Dropbox offers a freemium model for cloud storage. They provide a free basic service with limited storage and charge for premium plans with additional features and larger storage capacity. This model attracts a wide user base while monetizing the more demanding users.
Marketplace Business Model
Example: eBay
Description: eBay operates as an online marketplace connecting buyers and sellers. They facilitate transactions and earn a fee or commission on each successful sale. This model thrives on a large and diverse user base.
Franchise Business Model
Example: McDonald’s
Description: McDonald’s is a franchise-based business model. They grant individuals (franchisees) the right to operate McDonald’s restaurants using the company’s brand, products, and systems. Franchisees pay fees and royalties to the parent company.
Razor and Blade Business Model
Example: Gillette
Description: Gillette’s razor and blade model involves selling razors at a low cost (or sometimes even giving them away) and making profits from selling replacement razor blades, which are proprietary and more expensive. It encourages customer lock-in and repeat purchases.
Crowdsourcing Business Model
Example: Kickstarter
Description: Kickstarter is a crowdsourcing platform that allows creators to fund their projects through contributions from the public. Creators set funding goals, and backers contribute money. If the goal is met, the project is funded. Kickstarter takes a percentage of the funds raised.
Summing Up
The “business plan” and “business model” discussed above are useful allies in your entrepreneurial pursuits rather than opposing elements. The business model specifies the final goal, whereas the business plan outlines the journey. Understanding this distinction can make all the difference when starting or developing an established firm.
As a digital agency specializing in business planning, we understand that writing a successful business plan requires expertise. Our specialists help you transform your company plan into an effective blueprint.
Are you ready to advance the operations of your business? Get in touch with us toady!. Together, let’s strive to realize your dreams.

